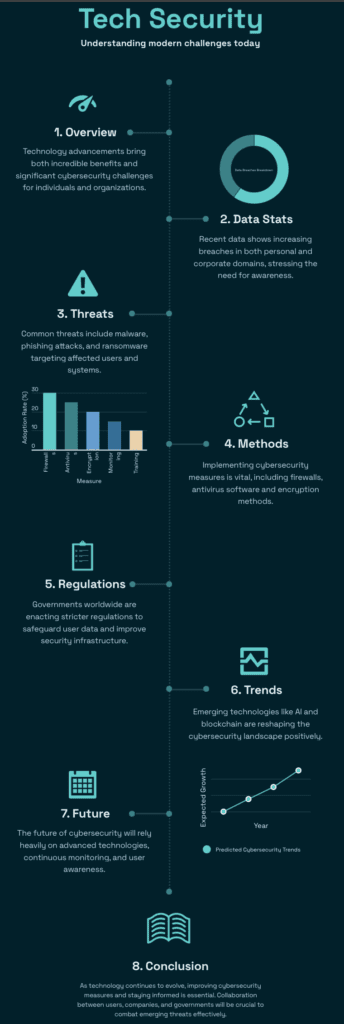
In today’s digital age, cybersecurity is more critical than ever. As businesses, governments, and individuals rely increasingly on the internet, the risks associated with cyber threats continue to grow. Hackers are becoming more sophisticated, and the frequency of cyberattacks is rising, leading to significant losses for companies and individuals alike. From data breaches and ransomware attacks to identity theft and fraud, the landscape of cybersecurity challenges is ever-evolving.
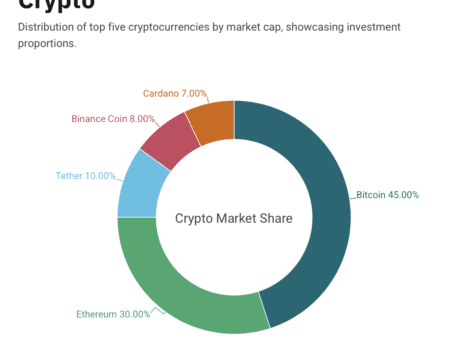
While traditional security measures, such as firewalls, encryption, and multi-factor authentication, remain essential, the need for innovative solutions to combat modern cyber threats is pressing. One such solution that has gained significant attention in recent years is blockchain technology. Although blockchain is commonly associated with cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum, its potential for enhancing cybersecurity is vast. In this post, we will explore the role of blockchain in cybersecurity and how it can positively impact the way we secure sensitive data and protect against cyber threats.
Understanding Blockchain Technology
Blockchain is a decentralized, distributed ledger that records transactions across many computers in a way that ensures security, transparency, and immutability. Unlike traditional centralized systems, where a central authority (e.g., a bank or company) manages the data, blockchain operates on a peer-to-peer network where all participants have access to the same information. Each transaction is recorded in a “block,” and these blocks are linked together in a chronological order, forming a “chain.”
One of the key features of blockchain is its use of cryptographic techniques to secure transactions and data. Each block contains a unique cryptographic hash, which is a digital signature that ensures the data inside the block has not been altered. Once a block is added to the blockchain, it is nearly impossible to modify or delete the information it contains, providing an immutable and secure record of all transactions.
The decentralized and transparent nature of blockchain makes it a powerful tool for addressing many of the challenges faced in cybersecurity today. By eliminating the need for a central authority and using cryptographic techniques, blockchain can provide a more secure, tamper-resistant solution for protecting data.
Blockchain’s Positive Impact on Cybersecurity
1. Decentralization and Reduced Risk of Single Points of Failure
One of the most significant advantages of blockchain technology is decentralization. In traditional centralized systems, a central server or database stores all the data, which makes it a prime target for hackers. If a cybercriminal can breach the central server, they gain access to sensitive data, potentially compromising the entire system. This is known as a single point of failure.
Blockchain’s decentralized nature eliminates this risk by distributing data across a network of nodes (computers). Each node stores a copy of the blockchain, and any changes to the data must be validated by the majority of participants in the network. This means that even if one node is compromised, the data is still secure, as the information remains consistent across the other nodes.
Moreover, the consensus mechanisms used in blockchain (e.g., Proof of Work, Proof of Stake) ensure that malicious actors cannot easily alter the data or disrupt the network. For instance, to successfully manipulate a blockchain, an attacker would need to control more than 50% of the network, which is practically impossible in most large blockchain networks.
2. Immutability and Tamper Resistance
Another key feature of blockchain is its immutability. Once a transaction is recorded on the blockchain, it cannot be changed or deleted. This is a game-changer for cybersecurity, as it makes it extremely difficult for hackers to alter or tamper with the data.
In the context of cybersecurity, this immutability can be used to ensure the integrity of sensitive information, such as financial records, contracts, and identity data. For example, by recording transactions on a blockchain, companies can create an immutable audit trail that can be used to verify the authenticity of data and ensure that it has not been tampered with.
This immutability also makes blockchain an excellent tool for combating fraud and cyberattacks, as any attempt to alter the blockchain’s data would be immediately detectable by the network. As a result, blockchain can provide a higher level of confidence in the integrity of the data and prevent malicious actors from manipulating or falsifying records.
3. Enhanced Data Privacy and Security
Data privacy is a critical concern in the digital age, with personal information being collected and stored by companies, governments, and online platforms. Cyberattacks, such as data breaches, can expose sensitive data and lead to identity theft, financial fraud, and other malicious activities.
Blockchain can help enhance data privacy and security by allowing individuals to maintain control over their personal data. With blockchain, users can store their data in a decentralized manner, granting access to specific parties only when necessary. For example, a person could store their health records on a blockchain and allow a healthcare provider to access the information only when needed, without giving them full control over the data.
Additionally, blockchain uses cryptographic techniques to secure transactions and protect sensitive data. Public-key cryptography ensures that data can only be accessed by authorized parties, and blockchain’s decentralized nature means that there is no central authority that can be hacked and exposed to the risks of data breaches.
4. Blockchain for Identity Management
Identity theft is one of the most common forms of cybercrime, with criminals often using stolen personal information to commit fraud or gain unauthorized access to accounts. Blockchain can help prevent identity theft by providing a secure, decentralized way to manage digital identities.
In a blockchain-based identity management system, individuals would have control over their personal information and could use cryptographic keys to verify their identity. This would eliminate the need for centralized identity databases, which are often vulnerable to breaches and hacking attempts. Blockchain’s transparency and immutability also ensure that the information is accurate and cannot be tampered with, providing a more secure and reliable system for managing identities.
5. Smart Contracts and Automated Security
Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code. These contracts automatically execute when predefined conditions are met, reducing the need for intermediaries and increasing the efficiency of transactions.
In terms of cybersecurity, smart contracts can help automate security processes and ensure that transactions are carried out securely. For example, a smart contract could be used to automatically enforce the terms of a data-sharing agreement between two parties, ensuring that both parties comply with the agreed-upon terms before any data is exchanged. This reduces the risk of human error or malicious activity and ensures that transactions are conducted securely and transparently.
6. Blockchain for Secure Communications
Secure communication is vital in protecting sensitive information from cyberattacks. Blockchain can be used to enhance the security of communication channels by providing end-to-end encryption and ensuring that messages cannot be intercepted or altered during transmission.
By using blockchain-based messaging systems, individuals and organizations can securely exchange information without relying on centralized servers that could be vulnerable to attack. The decentralized nature of blockchain ensures that communication is not subject to the control of a single entity, making it more difficult for hackers to compromise the system.
As cyber threats continue to evolve, the need for innovative solutions to enhance cybersecurity is more pressing than ever. Blockchain technology offers a promising solution to many of the challenges faced in securing digital assets, protecting privacy, and ensuring the integrity of data. Its decentralized, transparent, and tamper-resistant nature makes it an ideal tool for combating cyberattacks and enhancing trust in digital systems.
From improving data security and privacy to enabling secure identity management and smart contracts, blockchain has the potential to revolutionize the way we approach cybersecurity. While blockchain is still an emerging technology, its positive impact on cybersecurity is already becoming clear, and as the technology continues to mature, we can expect even more significant advancements in the fight against cybercrime.